Have you ever experienced this situation: feeling severe foot fatigue and pain after walking for a short distance, making it difficult to continue? Do you often sprain your foot on the outer side, stumble, or even notice a visual discrepancy in the length of your legs, where one appears longer than the other? If so, there is a high chance you may have cavus foot.
01 What is Cavus Foot?
Cavus foot, also known as claw foot, is a common foot deformity observed in both adults and children. It is typically characterized by a shortened foot and an exaggerated upward arch in the middle of the foot. This condition represents an abnormal elevation of the foot arch. When standing and bearing weight, the pressure is concentrated on the heel and the ball of the foot, reducing the surface area of the sole that comes into contact with the ground, leading to pain.
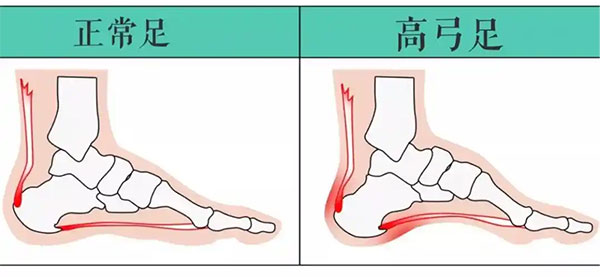
It is widely recognized that over 50% of cavus foot deformities result from neuromuscular imbalances and the consequent development of progressive or non-progressive deformities. Simply put, this condition is usually caused by nerve dysfunction and muscle strength imbalances in the foot. Additionally, improper gait, physical activity, and accidental injuries can exacerbate the formation of cavus foot.
02 How to Assess the Severity of Cavus Foot?
- Visual Inspection of the Heel
Compared to a normal foot structure, cavus foot shows a noticeable inward tilt of the calcaneus (heel bone) when viewed from the heel. As shown in the illustration, the larger the angle θ, the more pronounced the inversion, indicating a more severe case of cavus foot. 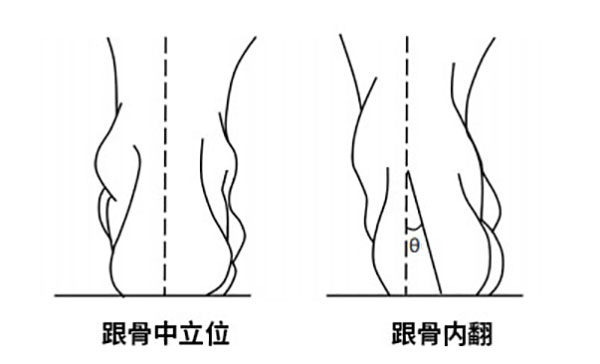
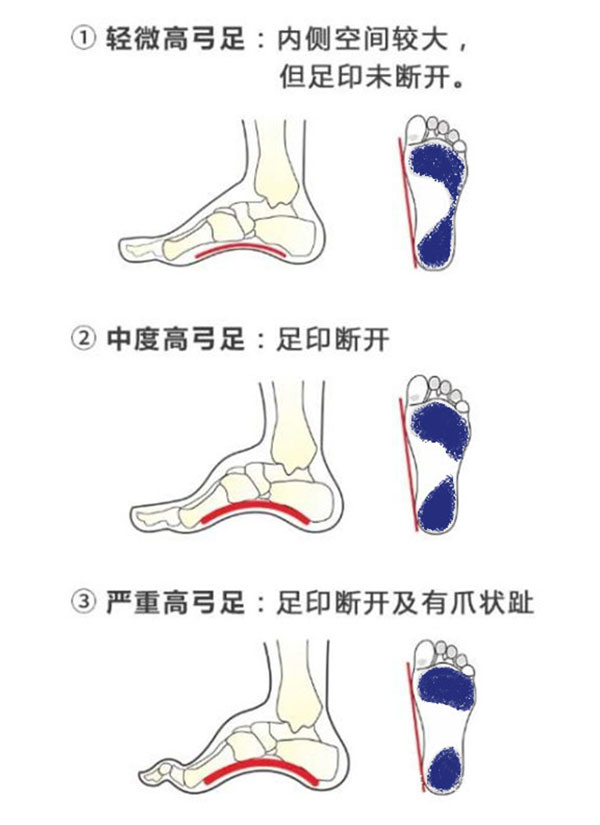
- Two-Foot Ink Test
Prepare a sheet of white paper and dip the soles of both feet in water (blue ink can be used for easier observation). Step onto the paper one at a time, leaving footprints. The shape of the footprints (blue areas shown in the illustration) can help determine the presence and extent of cavus foot.
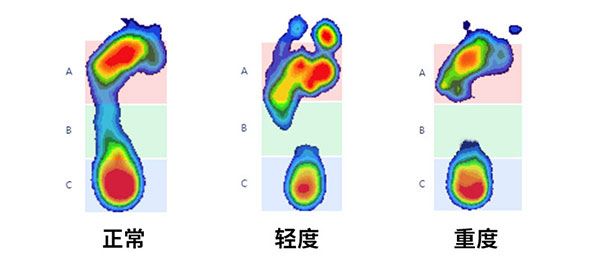
4. Static Pressure Testing
Use professional plantar pressure testing equipment to obtain precise pressure data while standing still. Based on the pressure distribution, the severity of cavus foot can be analyzed.Normal feet exhibit even pressure distribution, with noticeable force across the arch.In mild cases of cavus foot, a disconnection is observed between the forefoot and heel, appearing as a gap.The more severe the cavus foot, the larger the gap and the more significant the blank areas.
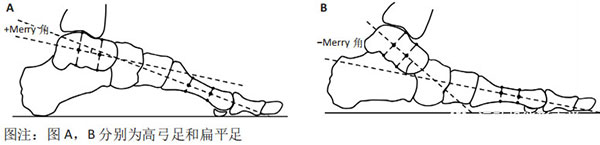
4. Weight-Bearing Lateral Foot X-Ray
Perform lateral foot measurements under weight-bearing conditions. This radiographic assessment is considered the most accurate method.
The Meary’s Angle, defined as the angle between the long axis of the talus and the first metatarsal, serves as the evaluation criterion:
- Under normal weight-bearing conditions, the Meary’s angle ranges between -4° and +4°.
- Meary’s angle > +4° indicates cavus foot.
- Meary’s angle < -4° indicates flatfoot.
03 Is It Necessary to Treat Cavus Foot?
If cavus foot doesn’t cause significant discomfort, no specific treatment may be needed. However, it is strongly recommended to manage your weight and choose supportive footwear!
Standard Treatment Principles:
- Biomechanical Corrective Insoles:
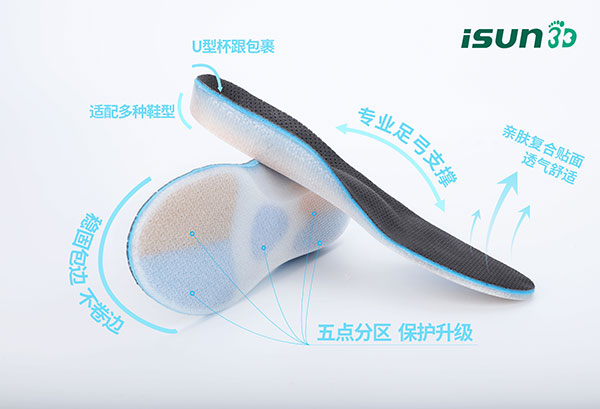

2. Functional Rehabilitation for Foot and Ankle:

3. Toe Spreading Exercises


